Scope & objective of Course :
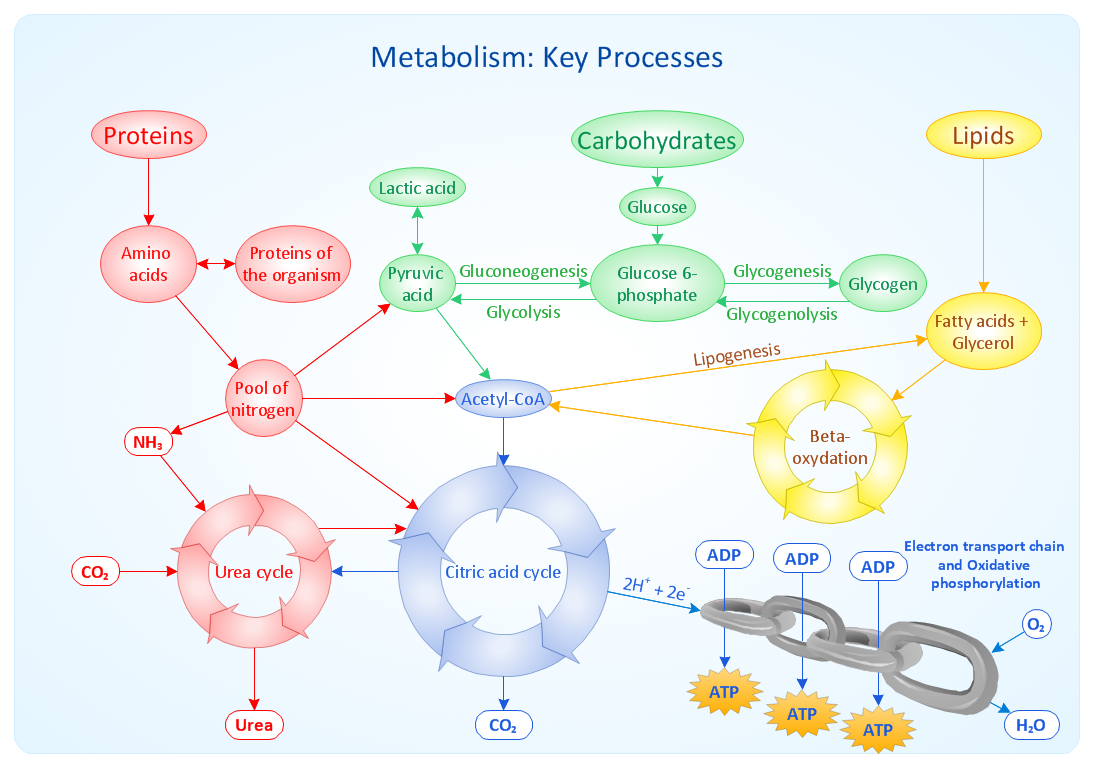
This course aims at understanding the essential metabolic functions of the human organism as well as and the molecular & biochemical basis of human diseases through analysis , the mechanisms of production, consumption and storage of energy, intermediary metabolism of main biomolecules and its regulatory mechanisms.
Learning Outcomes:
On completion of the course the student will be able to do the following:
CO1. Demonstrate an understanding of the metabolic pathways - the energy-yielding and energy requiring reactions in life.
CO2. Demonstrate an understanding of the diversity of metabolic regulation, and how this is specifically achieved in different cells.
CO3. Correlate the metabolic activity of tissues and organs with their function.
CO4. Understand and apply scientific reasoning in the chemical sciences
CO5. Describe and appreciate the modern techniques utilized in understanding the key mechanistic steps at atomic-level detail.
CO6. Describe how these biochemical processes are not isolated but tightly integrated, with specific control sites and key junctions.
CO7. List stages in the catabolism of food molecules and describe what occurs during each stage.
CO8. Be able to communicate scientific information effectively in writing.
- Teacher: Dr. PRATHYUSHA YAMARTHI
Course Summary Immunotechnology explains the basics of immunology
with their applications in the usage of antibody – antigen reactions such as
precipitation, agglutination, immune and radial diffusion. It also explains
various techniques commonly used in medical field such as western blotting,
ELISA, RIA, immunohistochemistry, etc. The cellular assays using the
principles, various methodology and their applications in medical field has
helped various physicians and scientists to understand the reaction as well as
mode of treatment. Course Outcomes CO 1: Students
will be able to understand about the principles of Immunotechnology. CO 2:
It will help them to understand about Antibody assays, their principles,
methodology and its applications. CO 3:
Students will be able to understand the various techniques like ELISA, RIA,
etc. commonly used in medical field. CO 4:
Students will be able to explain the application of cellular assays, their
principles, methodology and their applications. CO 5:
Students will be able to describe about human peripheral blood, mononuclear
cells, and cytotoxicity assays.

- Teacher: Dr. SRINATH NAGANATHAN
|
UNIT |
OBJECTIVES |
|
I |
Inorganic Chemistry: This course is to study about chemistry coordination complexes, Coordination number and Isomerism in coordination compounds. |
|
II |
Organic Chemistry: The course is designed to provide concepts in organic chemistry which includes synthesis and properties of carboxylic acids and nitro compounds. |
|
III |
Physical Chemistry: This course is designed to provide the basic concepts in physical chemistry which include Kholrausch’s law, Onsagar’s equation, Nernst equation and its applications. |
|
IV |
General Chemistry:The course is to study classification of pericyclic reactions, mechanism of the reactions and also include stereochemistry of the reactions(Enantiomers and Diastereomers) |
CORSE OUTCOMES:
Students will be able to
CO1: Explain the ligand field splitting of d-orbital in different complexes.
CO2: Discussthe effect of substituents on the acidity of carboxylic acids and phenols.
CO3: Explain the synthetic applications of acetoacetic ester.
CO4: Describe the structure of various metal carbonyl compounds.
CO5: ApplyNernst equation for calculating E.M.F of electrolytic cells.
CO6: Explain the electrocyclic and cycloaddition pericyclic reactions.
CO7: Identify the stereoselective reactions.
- Teacher: T NAVYA KUMARI
Objective of Course:
The Objective of this course is to enable the students who study for it to acquire advanced training in Microbiology and related areas, such as Parasitology and Immunology, in terms of acquiring knowledge of micro-organisms, laboratory skills.
Course Outcomes:
On completion of the course the student will be able
to:
CO1 - Learn about the various types of micro organisms and the major diseases they cause.
CO2 - Acquire knowledge about different types of microscopes to view and interpret slides.
CO3- Know various Culture media and their applications and also understand various physical and chemical means of sterilization.
CO4 - Explain the principles involving asepsis, disinfection, sterilization, pathogenicity.
CO5- Understand the overall organization of the immune system.
CO6 - Identify the main mechanisms of immune tolerance and autoimmunity.
CO7 - Identify the role of antigen presenting cells, lymphocytes, and phagocytic cells in immune responses.
CO8- Articulate and adhere to safe working practice in a mixed microbiology/immunology laboratory.
- Teacher: VARALAKSHMI V