|
CO1: The students will be able perform the time and frequency domain analysis of the signals in a digital communication system. CO2: The students will be able to a design of digital communication system. CO3: The students will be able to study the and plot the wave structures for different pulse modulations CO4: The students will be able to understand the basics of information theory, source coding techniques and calculate Entropy of source. CO5: The students will be able to determine the performance of line codes CO6: The students will be able to describe and determine the performance of different error control coding schemes for the reliable transmission of digital signals. CO7: The student will be able to understand various spreading techniques and determine bit error performance of various digital communication systems. CO8 :The students will be able to theoretical concepts of paging system, cellular telephone, global positioning satellite ,facsimile ,video text. CO9: Students will be able to study the properties of Fourier series ,complex Fourier transforms and sampling theorem.
|

- Teacher: SANDHYA -
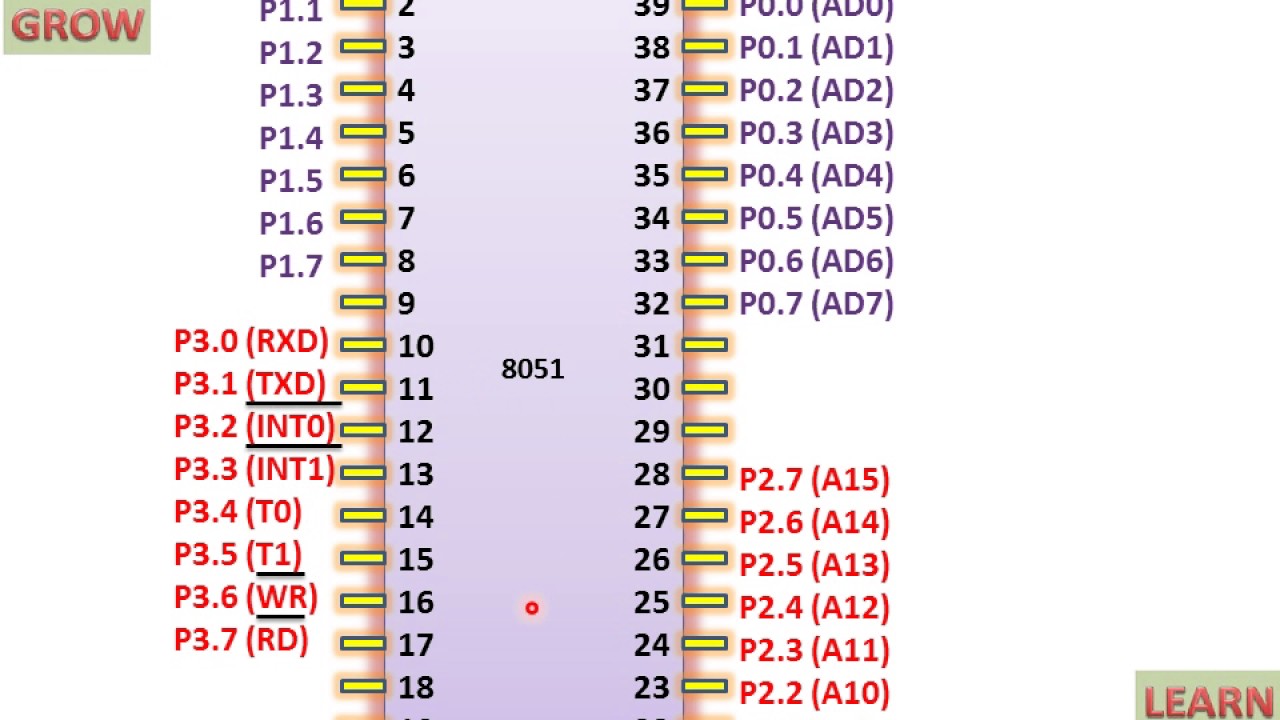
COURSE OBJECTIVES: COURSE
OUTCOMES: CO1: The students will be able
to understand what is a microcontroller,
microcomputer, embedded system and different components of micro-controller and
their interactions
- Teacher: SOWJANYA D
COURSE OBJECTIVES | |
1 | To provide students with an overview of the concepts and fundamentals of data communication and computer networks |
2 | To familiarize with the basic taxonomy and terminology of computer networking area. |
3 | Learn basic concepts of computer networking and acquire practical notions of protocols with the emphasis on TCP/IP. |
4
| A lab provides a practical approach to Client-Server networking: networks are assembled, and experiments are made to understand the layered architecture and how do some important protocols work. |
5 | Network configuration and management on UNIX |
COURSE OUTCOMES | |
CO1 | To master the terminology and concepts of the OSI reference model and the TCP‐IP reference model. |
CO2 | To master the concepts of protocols, network interfaces, and design/performance issues in local area networks and wide area networks |
CO3 | To be familiar with wireless networking concepts |
CO4 | To be familiar with contemporary issues in networking technologies |
CO5 | To be familiar with network tools and network programming |
CO6 | Familiarity with the basic protocols of computer networks, and how they can be used to assist in network design and implementation. |
- Teacher: NOOR UNISA
|
COURSE OBJECTIVES |
|
|
1 |
To provide students with an overview of the concepts and fundamentals of data communication and computer networks |
|
2 |
To familiarize with the basic taxonomy and terminology of computer networking area. |
|
3 |
Learn basic concepts of computer networking and acquire practical notions of protocols with the emphasis on TCP/IP. |
|
4
|
A lab provides a practical approach to Client-Server networking: networks are assembled, and experiments are made to understand the layered architecture and how do some important protocols work. |
|
5 |
Network configuration and management on UNIX |
|
COURSE OUTCOMES |
|
|
CO1 |
To master the terminology and concepts of the OSI reference model and the TCP‐IP reference model. |
|
CO2 |
To master the concepts of protocols, network interfaces, and design/performance issues in local area networks and wide area networks |
|
CO3 |
To be familiar with wireless networking concepts |
|
CO4 |
To be familiar with contemporary issues in networking technologies |
|
CO5 |
To be familiar with network tools and network programming |
|
CO6 |
Familiarity with the basic protocols of computer networks, and how they can be used to assist in network design and implementation. |

- Teacher: NOOR UNISA
Course Objective
The objective of this course is to provide a classroom and laboratory environment that enables students to develop basic skills in web-based programming and to gain experience on the same. This course will help the student to
· Appreciate and learn the fundamentals and advanced web-based concepts.
· Effortless designing Skills involved in web programming.
· Ease with page development and DVV.
Course outcome
Each Student is expected to possess the following caliber individually after successful completion of the course.
CO1 To understand web based programming
CO2 To learn the syntax, semantics, and the structure of the HTML.
CO3 Clarity in Understanding TAGS, Scripts.
CO4 Ability to describe and implement web and scripts concepts.
CO5 Understand the Web of structure
CO6 Proficient enough to understand and implement web-based challenges.

- Teacher: JAIMOLE CROSS
- Teacher: VIDYA SAGAR JODU
- Teacher: KAYAL Padmanandam
Course Objective
1 Enrich the knowledge of mathematical skills to the students in the areas of numerical methods. 2 To teach theory and applications of numerical methods in a large number which require solutions of interpolation and ODEs.
Course Outcomes
CO1 Solve the algebraic and transcendental equations using bisection method, method of false position and Newton-Raphson method. CO2 Familiar with calculation of errors in numerical method by Muller’s method. CO3 Evaluate the functional value by using Lagrange interpolation for unequal intervals. CO4 Apply Hermite and cubic spline interpolation to define polynomial on sub-intervals. CO5 Evaluate differention using difference table. CO6 Familiar with numerical solution of ordinary differential equations.

- Teacher: NAGENDRA KUMAR GOLLAPUDI
Course Objective:
1. Apply integration to evaluate work done, area and volume of a vector field
2. Analyze gradient, divergence and curl to evaluate the differentiation over a vector field
Course Outcomes:
After the
completion of the course the student will be able to
CO1: Apply single integration to find the work done of the vector field
CO2: Evaluate surface area using double integration
CO3: Determine the volume of the given vector field using triple integral
CO4: Find partial derivatives and Taylor’s series to multivariable functions
CO5: Apply gradient operator to convert a scalar field into a vector filed
CO6: Analyze vector fields and compute divergence and curl

- Teacher: DAYANANDA BABU V