Course Description:
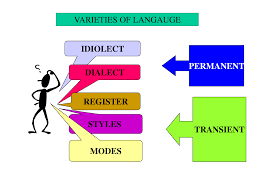
Varieties of English as part of the subject Communicative English for B.A (Vocational) course is designed keeping in view the real challenges students face in using English as a language of transaction. This Paper is intended to equip students with the knowledge of different aspects of language such as the origin of language, language as a communication tool, dialect, isogloss, registers, styles and various communication patterns. Besides the theoretical aspect, the syllabus also includes practical component in the form of conversations and dialogues. A thorough study of the topics and participation in the class-room activities and doing the exercises will help students acquire knowledge over the various elements of the language as well as help them gain mastery over the use of English.
Course Outcomes:
The students will be able to:
CO I. Understand the concept of Language – differentiate it from other forms of communication
CO II. Learn about the British and American English – the differences in vocabulary, spelling, pronunciation and grammar.
CO III. Understand the circumstances in which a bilingual switches languages and mixes words from two or three different languages to facilitate better understanding of a situation.
CO IV. Distinguish between the formal and the informal styles of communication.
CO V. Identify the circumstances in which register variations take place.
CO VI. Learn about the evolution of language-both spoken and written- with special reference to written English.
CO VII. Study Charles Hockette’s design that characterizes human language.
CO VIII. Understand the fundamentals of Communication with emphasis on Oral, Written, Audiovisual and Visual communication.
- Teacher: JOSEPH CHRISTADOSS T
Course Objective: This course offers an overview of the concepts and practices associated journalistic writing forms. The engagement is both theoretical and practical in nature where the learners are expected to understand the concepts and apply the methods to develop their skills in journalistic writing. The course should enable and inspire the learners to develop a knack for picking up story ideas which are of publishable standards across the print and new media. The idea is to introduce and expose them to the nuances of different forms of writing related to journalism. The engagement is on the basis of dialogue and delivery while the topics are explored together through focused lectures, periodic writing and editing assignments.
Course Outcome: By the end of this course, the student should be able to-
Ø Identify different types of news and feature stories and elements of news writing;
Ø Understand subjectivity and objectivity in writing, when and where to apply them;
Ø Write different forms of feature stories for news;
Ø Edit different kinds of feature stories and present them in acceptable formats;
- Teacher: AMRIT AMLAN PATTANAIK
INDIAN POLITICAL THOUGHT
CREDITS-5
Name of the Faculty: Mr. K.T.Srinivas.
Assistant Professor of Political Science ( 17 years’ experience)
Unit-I: State and Society in India.
Syllabus: 1) Manu- Features of Manusmrithi, origins of Varna, Varna
Dharma.
2) Buddha : Dhamma , Sangha, Eight fold path.
3) Kautilya- Saptanga theory, Mandala theory, Statecraft.
Objectives of the study:
· The central aims in this chapter will be to gain a critical perspective on our times by evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of Manu , Buddha and Kautilya’s philosophical approaches.
· This Module examines major texts in the history of political thought, written by Manu , Buddha and Kautilya. Many of these texts discuss difficult questions concerning the political community, social order, and human nature.
· It also considers the ways in which thinkers like Manu , Buddha and Kautilya, have responded to the political process of their times, and the ways in which they contribute to a broader conversation about human goods and needs, justice, and the ever-changing relationship between the citizen and the state.
Learning outcomes;.
|
After going through this Module, a student will be able to: · Explain the political thought of Manu, Buddha and Kautilya ,and also implement some of them in his real Life situations and enrich life. |
· For a good student, ,the study of this chapter will increase awareness of career options available with an undergraduate degree in Political Science, its utility in securing jobs in public and private sectors, and also equip them in their future education( to pursue their masters degree and PhD in Political Science
· For an average student, the study will be helpful to be a better citizen, enable him to pass the exam and acquire a degree.
Unit -2, Medieval Political Thought.
Syllabus: 1) Basava- Anubhava Manatapa, Gender
Equality.
2) Zaiuddin Barani- Theory of Kingship(Ideal
Sultan), Ideal Polity.
Objectives of the study:
· The central aim in this chapter will be to gain a critical perspective on our times by evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of Basava and Zaiuddin Barani’s philosophical approaches to social and political issues.
· We will also work to better understand Basava and Zaiuddin Barani’s assumptions and basic concepts that define the field of political science.
· This Module examines major texts in the history of Medieval political thought. Many of these texts pose difficult questions concerning the political community, social order, and human nature.
· It also considers the ways in which thinkers like Basava and Zaiuddin Barani responded to the political and social problems of their times, and the ways in which they contribute to a broader conversation about human goods and needs, justice, administration, and the ever-changing relationship between the citizen and the state.
· Learning outcomes;
· The student will be able to explain the political thought, of Basava and Zaiuddin Barani.
· Apply Basava and Zaiuddin Barani’s ideas to the present day problems of the state and society.
· For a good student, ,the study of this chapter will increase awareness of career options available with an undergraduate degree in Political Science, its utility in securing jobs in public and private sectors, and also equip them in their future education( to pursue their master’s degree and PhD in Political Science) or to acquire them a professional degree( ex; Law).
· For an average student, the study will be helpful to be a better citizen, enable him to pass the exam and acquire a degree
Unit–3, Renaissance Thought
· Raja Ramohan Roy-Colonial encounters, Brahmao Samaj.
· Jyothi Rao Phule- Gulam Giri, Satya Shodak Samaj, Education.
Objectives of the study:
· The study of this unit enables the student to increase the understanding of basic ideas and concepts explained by Raja Ramohan Roy and Jyothi Bai Phule in the books written by them.
· The central aims in this chapter will be to gain a critical perspective on our times by evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of Raja Ramohan Roy and Jyothi Bai Phule thought in our daily political and social life of our country.
· We will also work to better understand those assumptions and basic concepts that define the field of political science and how to implement the social reforms they advocated during their time. These social problems like untouchability, widow’s plight are still prevalent in the present society.
Learning outcomes;
· Student will be in a position to explain the political thought, of Raja Ramohan Roy and Jyothi Ba Phule
· Apply Raja Ramohan Roy and Jyothi Bai Phule’s ideas to the present day problems of the state.
· For a good student, ,the study of this chapter will increase awareness of career options available with an undergraduate degree in Political Science, its utility in securing jobs in public and private sectors, and also equip them in their future education( to pursue their master’s degree and PhD in Political Science) or to acquire them a professional degree( ex; Law).
· For an average student, the study will be helpful to be a better citizen, enable him to pass the exam and acquire a degree
Unit -4 Reformist Thought
Syllabus
· M.K.Gandhi: Satyagraha, Trusteeship, Problem of Political Obligation.
· Dr.B.R.Ambedkar: Who are Sudhras? Annihilation of caste.
Objectives of the study:
· The central aims in this chapter will be to gain a critical perspective on our times by evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of various philosophical approaches, of M.K.Gandhi and Dr. B.R.Ambedkar.
· We will also work to better understand those assumptions and basic concepts of M.K.Gandhi and Dr. B.R.Ambedkar. that define the field of political thought.
· This Module examines major texts in the history of political thought written by M.K.Gandhi and Dr. B.R.Ambedkar. Many of these texts pose difficult questions concerning the political community, social order, and human nature, and suggests solutions to social and
Political problems.
· It also considers the ways in which thinkers like M.K.Gandhi and Dr. B.R.Ambedkar. have responded to the political problems of their times, and the ways in which they contribute to a broader conversation about human goods and needs, justice, democracy, and the ever-changing relationship between the citizen and the state.
· Learning outcomes;
· Student will be in a position to explain the political thought, of thinkers M.K.Gandhi and Dr. B.R.Ambedkar.
· Explain the relationship between political thought and political science
· Apply ideas of M.K.Gandhi and Dr. B.R.Ambedkar to the present day problems of the state.
· For a good student, ,the study of this chapter will increase awareness of career options available with an undergraduate degree in Political Science, its utility in securing jobs in public and private sectors, and also equip them in their future education( to pursue their master’s degree and PhD in Political Science) or to acquire them a professional degree( ex; Law).
· For an average student, the study will be helpful to be a better citizen, enable him to pass the exam and acquire a degree.
Unit-5. SOCIALIST THOUGHT.
Syllabus:
· Manabendranath Roy(M.N.Roy)—Radical Humanism.
· Jawaharlal Nehru- Democratic Socialism.
· Ram Manohar Lohia: Concepts of four pillars of the
State.( Chaukhambe Model).
Objectives of the study:
· The central aims in this chapter will be to gain a critical perspective on our times by evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of various philosophical approaches,of M.N.Roy, Jawaharlal Nehru, Ramanohar Lohia.
· This Module examines major texts written by M.N.Roy, Jawaharlal Nehru, Ramanohar Lohia in the history of political thought. Many of these texts pose difficult questions concerning the political community, social order, and human nature and suggest solutions to political and social problems.
· It also considers the ways in which thinkers like M.N.Roy, Jawaharlal Nehru,Ramanohar Lohia. have responded to the political problems of their times, and the ways in which they contribute to a broader conversation about human goods and needs, justice, democracy, and the ever-changing relationship between the citizen and the state.
· Learning outcomes;
· Student will be in position to explain the political thought, of M.N.Roy, Jawaharlal Nehru ,Ramanohar Lohia.
· Apply ideas of M.N.Roy, Jawaharlal Nehru, Ramanohar Lohia to the present day problems of the state.
· For a good student, ,the study of this chapter will increase awareness of career options available with an undergraduate degree in Political Science, its utility in securing jobs in public and private sectors, and also equip them in their future education( to pursue their master’s degree and PhD in Political Science) or to acquire them a professional degree( ex; Law).
· For an average student, the study will be helpful to be a better citizen, enable him to pass the exam and acquire a degree.
*******
- Teacher: TIRUMALA SRINIVAS .K
Course Outcomes:
The students will be able to:
CO1 Use new concepts, vocabulary, and with appropriate grammar and structure
CO2 Become more empathetic channelizing their ideas towards positive attitude and actions
CO3 Articulate with greater display of Speaking and Writing skills
CO4Understand the relations between words and ideas
CO5 Develop interest in stories infused with moral purpose (attitudes and understandings that are beyond our own immediate experience)
CO6 Engaging with simple to complex writings & for understanding complex lives.
CO7 Literature and analyzing how times, cultural intentions and literary genres differ from one another.
CO8 Grasp the skills and theories of interpretation, with language and representation.
CO9 Listen, practice and hone English language skills to a great extent.

- Teacher: Dr MICHAEL PREETHAM JAKKULA
- Teacher: Dr. MAITHRY SHINDE
This course offers an overview of the basic concepts of communication and journalism, along with the necessary tools to understand and discuss their relevance in a fast changing mediated society.
Objectives:
· To develop nose for news.
· To impart journalistic skills to the students.
· To enable the students to understand the organizational structure of newspapers.
· To introduce editing.
· To familiarize the students with media law.
Learning Outcomes:
After completion of the course, the student will be able to:
· Identify different dimensions of the news.
· Edit the news reports.
· Explain the laws relating to media.

- Teacher: ARPITA SENGUPTA